

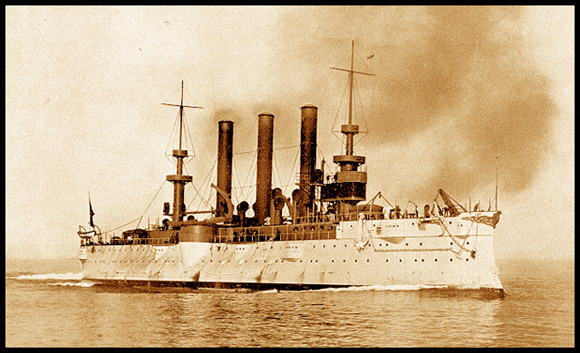
On July 3, 1898, USS BROOKLYN was a key vessel in the Battle of Santiago, which resulted in the loss of the Spanish fleet in the Caribbean. The ship's movements at the opening of the battle, directed by Commodore Schley, created controversy. In an effort to bring itself into position, BROOKLYN made a wide turn to starboard, away from the enemy and directly into a collision course with the USS TEXAS. A collision was narrowly avoided, and TEXAS was forced to cut speed at a critical moment. In spite of the unqualified success of the Flying Squadron that day, this maneuver would be discussed for years and used as evidence of Commodore Schley's incompetence.
After the war, USS BROOKLYN was present for the Spanish-American War Victory Celebration at New York on October 5, 1898, and the Dewey Celebration in September 1899. On October 16, 1899, BROOKLYN sailed for the Philippines, where she became the flagship of the Asiatic Squadron. She took part in the North China Relief Expedition ("Boxer Rebellion") in 1900.
In 1902, USS BROOKLYN returned to Cuba for the ceremony of the transfer of authority from the United States to a new Cuban government. She cruised with the North Atlantic Fleet and the European Squadron, becoming the flagship of Rear Admiral C. D. Sigsbee, the last commander of the ill-fated USS MAINE, on June 7, 1905. Under Sigsbee, she had the honor to sail to Cherbourg, France to return the remains of American Revolutionary War naval hero John Paul Jones to the United States.
In 1906, USS BROOKLYN was placed in reserve. She served as a permanent display at the famous 1907 Jamestown Exposition, from where the Great White Fleet left for its world cruise. USS BROOKLYN was decommissioned on June 23, 1908, but commissioned "in ordinary" in 1914 to serve as a receiving ship at the Boston Naval Yard. Fully recommissioned in 1915, she served as part of the Neutrality Patrol. Late that same year she was transferred to the Asiatic Station, where she served as flagship for the commander-in-Chief. Later she served various diplomatic functions, as well as the flagship for the Commander of Division 1, Asian Fleet, and later of the Commander of the Destroyer Squadron.
USS BROOKLYN was placed out of commission for the final time on March 9, 1921, and was sold on December 20, 1921.
The one criticism of USS BROOKLYN was the engine arrangement on board.
The ship had two of its main engines powering each of its two screws. At
the commencement of the Battle of Santiago, the forward engine on each
shaft was uncoupled, and the ship could not stop to couple them during
the battle. For this reason, the BROOKLYN, like the NEW
YORK, was operating at half speed during the battle.
| Classification: | Armored Cruiser, ACR-3 | |
|---|---|---|
| Keel Laid: | August 2, 1893 | |
| Completed: | February 11, 1896 | |
| Comissioned: | December 1, 1896 | |
| Rig: | Two military masts | |
| Armament: | Eight 8" guns | |
| Twelve 5" guns | ||
| Twelve 6-pounders | ||
| Four 1-pounders | ||
| Four Colt Gatling Guns (for landing parties) | ||
| Two 3" field pieces (for landing parties) | ||
| Four Whitehead 18" surface torpedo tubes | ||
| Contractor: | William Cramp & Sons, Philadelphia, PA. | |
| Length: | 402 feet 7 inches | |
| Beam: | 64 feet 8 1/2" | |
| Mean draft: | 24 feet | |
| Max. draft fully loaded: | 26 feet 2 inches | |
| Displacement: | 9,215 tons | |
| Complement: | 46 officers and 470 men under the command of Capt. F. A. Cook | |
| Engine type: | Twin screw, four vertical triple expansion engines | |
| with a 42 inch stroke generating 18,769 hp. | ||
| Boiler type: | Five double-ended and 2 single-ended cylindrical boilers. | |
| Speed: | 21.91 knots | |
| Coal bunker capacity: | 1,461 tons | |
| Normal coal supply: | 900 tons | |
| Coal endurance at 10 knots: | 5,110 nautical miles | |
| Armor: | Sides: 3", Turrets: 5.5", Barbettes: 4" to 8" | |
| Cost: | $2,986,000 |
Clerk of Joint Comittee on Printing, The Abridgement of Message from the President of the United States to the Two Houses of Congress, (Washington: Government Printing Office, 1899.
Naval History Department, Navy Department, Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships, (Washington DC: Government Printing Office, 1959).